Backend Nest JS
Introduction 🚀
Welcome to the SOS NestJS Server with PostgreSQL documentation! This guide is designed to help developers seamlessly
integrate a powerful and efficient backend using NestJS and PostgreSQL. Whether you're building a new project or
enhancing an existing one, this document provides all the necessary steps, best practices, and troubleshooting tips to
ensure success.
Prerequisites 📎
-
Git (>= 2.x)
-
Node JS (>= 18.x)
-
Nest CLI (>= 1.x)
-
PostgreSQL (>= 14.x)
-
Basic knowledge of TypeScript, Node.js, Nest JS with Express platform and PostgreSQL
Setup Instructions (local)
Project Initialization
- Clone
sos-nest-tsproject github:
git clone https://github.com/simplyhomes/sos-nest-ts
- Navigate to the project directory:
cd sos-nest-ts
- Install
node_module:
yarn install
- Start project:
yarn run dev
Project structure and organization 💫
Folder and file conventions
Top-level folder
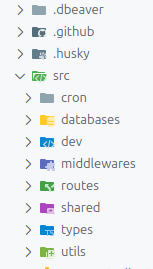
.dbever.github.huskysrccrondatabasesdevmiddlewaresroutessharedtypesutilsTop-level files
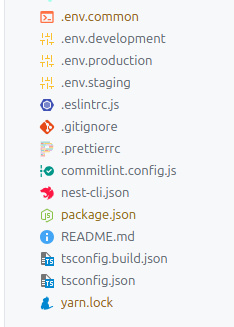
.env.common.env.development.env.production.env.staging.eslintrc.js.gitignore.prettierrccommitlint.config.jsnest-cli.jsonpackage.jsonREADME.mdtsconfig.build.jsontsconfig.jsonyarn.lockTesting APIs with Swaggers Docs 📂
Swagger UI
Swagger UI is a tool that visually renders documentation for APIs defined in the OpenAPI Specification. It provides a user-friendly interface to explore and test API endpoints, request parameters, and responses. The Swagger UI is automatically generated based on the API routes and schemas defined in the application.
To access the Swagger UI, navigate to the following URL in your browser:
http://localhost:5001/api
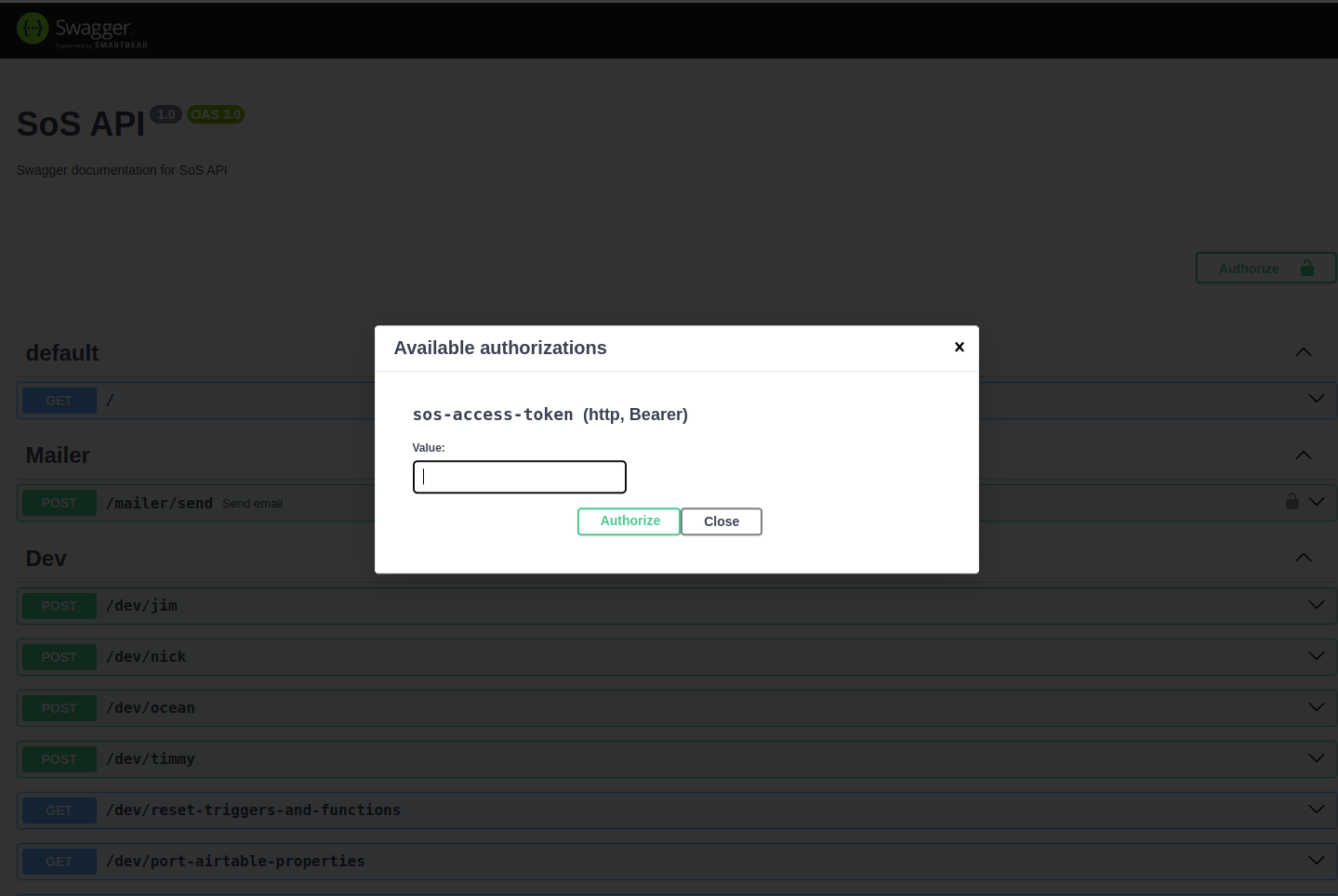
How to access the APIs via Swagger UI ?
Access token
Click on the Authorize button in the top right corner of the Swagger UI page. Enter the access token in the Value field and click Authorize.
Create a new API 🔥
Define a new route in the controller file of routes folder
Example:
@Patch(':nid/read')
@ApiOperation({ summary: 'Mark a notification as read' })
changeNotificationReadStatus(
@Param() query: Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Param_Dto,
@Body() body: Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Body_Dto
): Promise<Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Response_Dto> {
return this.notificationService.changeNotificationReadStatus({ ...query, ...body });
}
Explanation:
-
@Patch(':nid/read'): HTTP method and route path for the API endpoint, you can use@Get,@Post,@Put,@Delete,@Patchetc. -
@ApiOperation({ summary: 'Mark a notification as read' }): Description of the API endpoint, which will be displayed in the Swagger UI. -
changeNotificationReadStatus(): Method name for the API endpoint. -
@Param() query: Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Param_Dto: Request parameters defined in the DTO (Data Transfer Object) for the API endpoint. -
@Body() body: Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Body_Dto: Request body defined in the DTO (Data Transfer Object) for the API endpoint. -
Promise<Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Response_Dto>: Response type defined in the DTO (Data Transfer Object) for the API endpoint.
Define the DTO (Data Transfer Object) for the request and response payloads
Example:
import { Transform } from 'class-transformer';
import { IsBoolean, IsNumber } from 'class-validator';
export class Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Param_Dto {
@Transform(({ value }) => parseInt(value))
@IsNumber()
nid!: number;
}
export class Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Body_Dto {
@Transform(({ value }) => Boolean(value))
@IsBoolean()
read!: boolean;
}
export class Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Response_Dto {
message!: string;
}
export type Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Params = Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Param_Dto &
Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Body_Dto;
export type Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Return = Promise<Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Response_Dto>;
Explanation:
-
Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Param_Dto: DTO class for request parameters. -
Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Body_Dto: DTO class for request body. -
Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Response_Dto: DTO class for response payload. -
@Transform(({ value }) => parseInt(value)): Decorator to transform the parameter value to an integer. -
@IsNumber(): Decorator to validate the parameter value as a number. -
@Transform(({ value }) => Boolean(value)): Decorator to transform the body value to a boolean. -
@IsBoolean(): Decorator to validate the body value as a boolean. -
message!: string;: Response message property. -
Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Params: Type definition for combined request parameters and body. -
Nofs_ChangeNotificationReadStatus_Return: Type definition for the API response.
Create a new service file in the services
Handle the business logic and data processing for the API endpoint in the service file.